18 KiB
| title | description | position | category | menuTitle | link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation | Simple installation - takes about three minutes! | 10 | Getting started | Installation | https://codesandbox.io/embed/vigorous-firefly-80kq5?hidenavigation=1&theme=dark |
Simple installation - takes about three minutes!
Prerequisites
- Must haves
- Nice to haves
- MySQL / Postgres / SQL Server / SQLite Database
- Existing schemas can help to create APIs quickly.
- An example database schema can be found here.
Quick try
1-Click Deploy to Heroku
Before doing so, make sure you have a Heroku account. By default, an add-on Heroku Postgres will be used as meta database. You can see the connection string defined in DATABASE_URL by navigating to Heroku App Settings and selecting Config Vars.
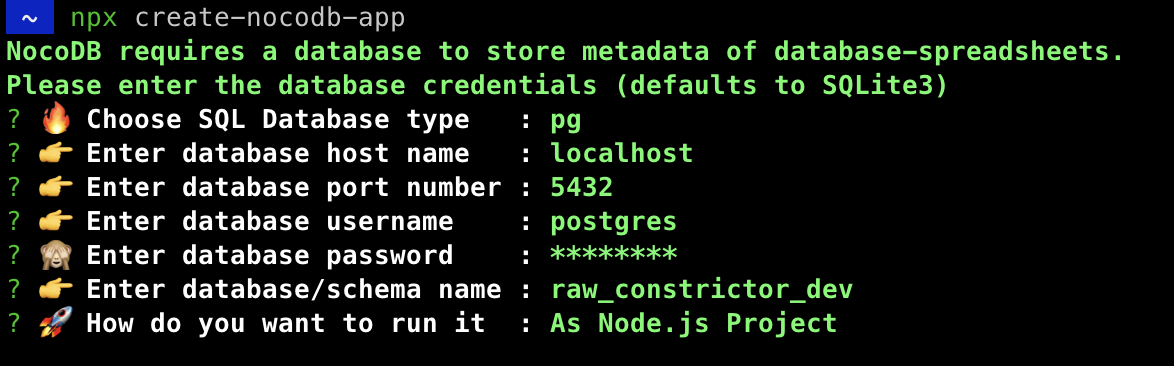
NPX
You can run below command if you need an interactive configuration.
npx create-nocodb-app
Preview:
Node Application
We provide a simple NodeJS Application for getting started.
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb-seed
cd nocodb-seed
npm install
npm start
Docker
If you are a Docker user, you may try this way!
docker run -d --name nocodb \
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \
-p 8080:8080 \
nocodb/nocodb:latest
docker run -d --name nocodb-mysql \
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e NC_DB="mysql2://host.docker.internal:3306?u=root&p=password&d=d1" \
-e NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET="569a1821-0a93-45e8-87ab-eb857f20a010" \
nocodb/nocodb:latest
docker run -d --name nocodb-postgres \
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e NC_DB="pg://host.docker.internal:5432?u=root&p=password&d=d1" \
-e NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET="569a1821-0a93-45e8-87ab-eb857f20a010" \
nocodb/nocodb:latest
docker run -d --name nocodb-mssql \
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e NC_DB="mssql://host.docker.internal:1433?u=root&p=password&d=d1" \
-e NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET="569a1821-0a93-45e8-87ab-eb857f20a010" \
nocodb/nocodb:latest
Docker Compose
We provide different docker-compose.yml files under this directory. Here are some examples.
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb
cd nocodb/docker-compose/mysql
docker-compose up -d
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb
cd nocodb/docker-compose/pg
docker-compose up -d
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb
cd nocodb/docker-compose/mssql
docker-compose up -d
Production Setup
By default, SQLite is used for storing meta data. However, you can specify your own database. The connection params for this database can be specified in NC_DB environment variable. Moreover, we also provide the below environment variables for configuration.
Environment variables
| Variable | Mandatory | Comments | If absent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID | No | For Litestream - S3 access key id | If Litestream is configured and NC_DB is not present. SQLite gets backed up to S3 | |
| AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | No | For Litestream - S3 secret access key | If Litestream is configured and NC_DB is not present. SQLite gets backed up to S3 | |
| AWS_BUCKET | No | For Litestream - S3 bucket | If Litestream is configured and NC_DB is not present. SQLite gets backed up to S3 | |
| AWS_BUCKET_PATH | No | For Litestream - S3 bucket path (like folder within S3 bucket) | If Litestream is configured and NC_DB is not present. SQLite gets backed up to S3 | |
| DB_QUERY_LIMIT_DEFAULT | No | Default pagination limit | 25 | |
| DB_QUERY_LIMIT_MAX | No | Maximum allowed pagination limit | 100 | |
| DB_QUERY_LIMIT_MIN | No | Minimum allowed pagination limit | 1 | |
| DATABASE_URL | No | JDBC URL Format. Can be used instead of NC_DB. Used in 1-Click Heroku deployment | ||
| DATABASE_URL_FILE | No | path to file containing JDBC URL Format. Can be used instead of NC_DB. Used in 1-Click Heroku deployment | ||
| PORT | No | For setting app running port | 8080 |
|
| NC_DB | Yes | See our database URLs | A local SQLite will be created in root folder | |
| NC_DB_JSON | Yes | Can be used instead of NC_DB and value should be valid knex connection JSON |
||
| NC_DB_JSON_FILE | Yes | Can be used instead of NC_DB and value should be a valid path to knex connection JSON |
||
| NC_DASHBOARD_URL | No | Custom dashboard url path | /dashboard |
|
| NC_TOOL_DIR | No | App directory to keep metadata and app related files | Defaults to current working directory. In docker maps to /usr/app/data/ for mounting volume. |
|
| NC_PUBLIC_URL | Yes | Used for sending Email invitations | Best guess from http request params | |
| NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET | Yes | JWT secret used for auth and storing other secrets | A Random secret will be generated | |
| NC_JWT_EXPIRES_IN | No | JWT token expiry time | 10h |
|
| NC_CONNECT_TO_EXTERNAL_DB_DISABLED | No | Disable Project creation with external database | ||
| NC_INVITE_ONLY_SIGNUP | No | Allow users to signup only via invite url, value should be any non-empty string. | ||
| NC_BACKEND_URL | No | Custom Backend URL | http://localhost:8080 will be used |
|
| NC_REQUEST_BODY_SIZE | No | Request body size limit | 1048576 |
|
| NC_EXPORT_MAX_TIMEOUT | No | After NC_EXPORT_MAX_TIMEOUT csv gets downloaded in batches | Default value 5000(in millisecond) will be used | |
| NC_DISABLE_TELE | No | Disable telemetry | ||
| NC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID | No | Google client id to enable google authentication | ||
| NC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET | No | Google client secret to enable google authentication | ||
| NC_MIGRATIONS_DISABLED | No | Disable NocoDB migration | ||
| NC_ONE_CLICK | No | Used for Heroku one-click deployment | ||
| NC_MIN | No | If set to any non-empty string the default splash screen(initial welcome animation) and matrix screensaver will disable | ||
| NC_SENTRY_DSN | No | For Sentry monitoring | ||
| NC_DISABLE_ERR_REPORT | No | Disable error reporting | ||
| NC_REDIS_URL | No | Custom Redis URL. Example: redis://:authpassword@127.0.0.1:6380/4 |
Meta data will be stored in memory | |
| NC_DISABLE_CACHE | No | To be used only while debugging. On setting this to true - meta data be fetched from db instead of redis/cache. |
false |
|
| NC_BASEURL_INTERNAL | No | Used as base url for internal(server) API calls | Default value in docker will be http://localhost:$PORT and in all other case it's populated from request object |
AWS ECS (Fargate)
Create ECS Cluster
aws ecs create-cluster \
--cluster-name <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER>
Create Log group
aws logs create-log-group \
--log-group-name /ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>
Create ECS Task Definiton
Every time you create it, it will add a new version. If it is not existing, the version will be 1.
aws ecs register-task-definition \
--cli-input-json "file://./<YOUR_TASK_DEF_NAME>.json"
Here's the sample Task Definition
{
"family": "nocodb-sample-task-def",
"networkMode": "awsvpc",
"containerDefinitions": [{
"name": "<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>",
"image": "nocodb/nocodb:latest",
"essential": true,
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>",
"awslogs-region": "<YOUR_AWS_REGION>",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
},
"secrets": [{
"name": "<YOUR_SECRETS_NAME>",
"valueFrom": "<YOUR_SECRET_ARN>"
}],
"environment": [{
"name": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME>",
"value": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_VALUE>"
}],
"portMappings": [{
"containerPort": 8080,
"hostPort": 8080,
"protocol": "tcp"
}]
}],
"requiresCompatibilities": [
"FARGATE"
],
"cpu": "256",
"memory": "512",
"executionRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_EXECUTION_ROLE_ARN>",
"taskRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_TASK_ROLE_ARN>"
}
Create ECS Service
aws ecs create-service \
--cluster <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER> \
--service-name <YOUR_SERVICE_NAME> \
--task-definition <YOUR_TASK_DEF>:<YOUR_TASK_DEF_VERSION> \
--desired-count <DESIRED_COUNT> \
--launch-type "FARGATE" \
--platform-version <VERSION> \
--health-check-grace-period-seconds <GRACE_PERIOD_IN_SECOND> \
--network-configuration "awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=["<YOUR_SUBSETS>"], securityGroups=["<YOUR_SECURITY_GROUPS>"], assignPublicIp=ENABLED}" \
--load-balancer targetGroupArn=<TARGET_GROUP_ARN>,containerName=<CONTAINER_NAME>,containerPort=<YOUR_CONTAINER_PORT>
Development Setup
If you want to modify the source code,
- Start the backend locally
cd packages/nocodb
npm install
npm run watch:run
- Start the frontend locally
cd packages/nc-gui
npm install
npm run dev
- Open
localhost:3000/dashboardin browser
You can visit localhost:8000/dashboard in browser after starting the backend locally if you just want to modify the backend only.