---
title: 'Dashboard'
description: 'Dashboard'
position: 500
category: 'Product'
menuTitle: 'Dashboard'
---
## Setup Your First Super Admin
Once you have started NocoDB, you can visit the dashboard via `example.com/dashboard`.
Click `Let's Begin` button to sign up.

Enter your work email and your password.
Your password has at least 8 letters with one uppercase, one number and one special letter
## Initialize Your First Project
Once you have logged into NocoDB, you should see `My Projects`.
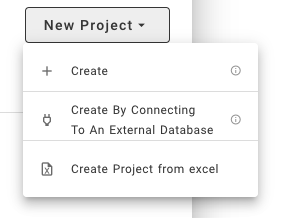
To create a project, you can click `New Project`.
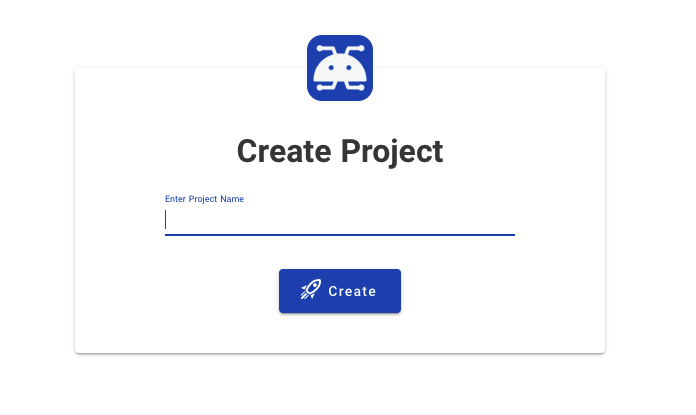
### Creating Empty Project
Click `Create`, you need to specify the project name and API type.
A local SQLite will be used.
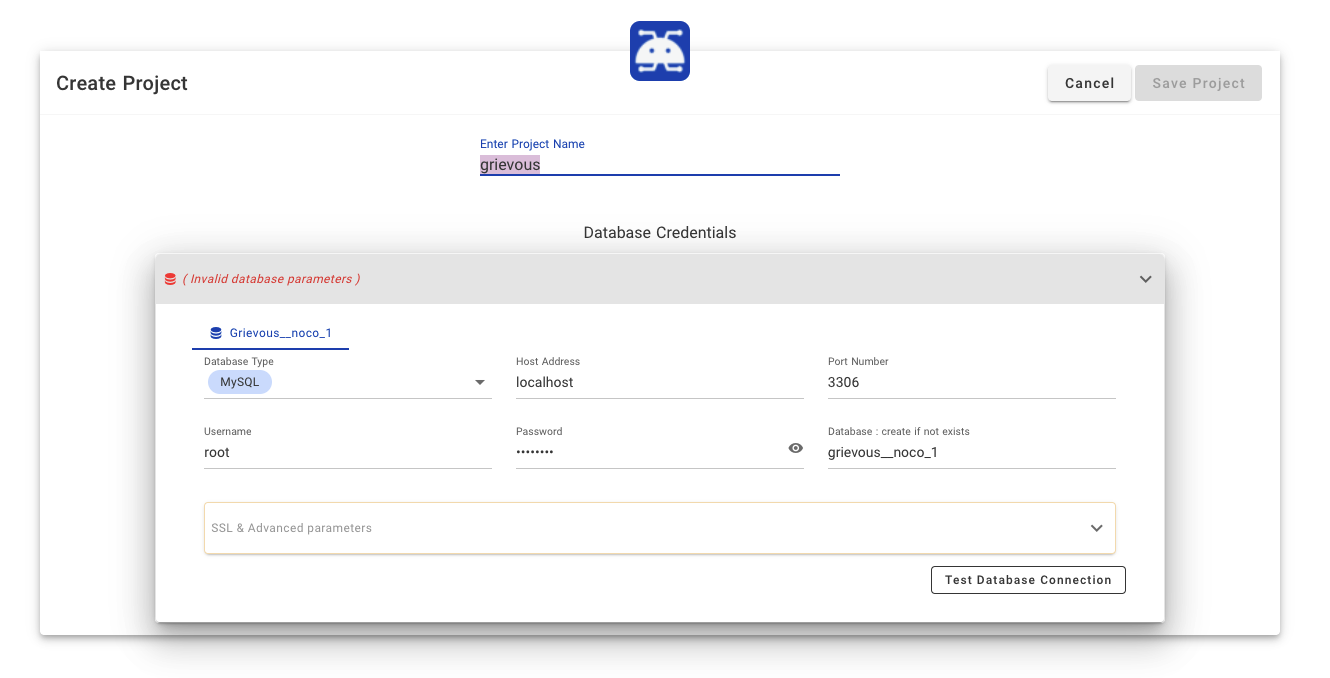
### Connecting to External Database
Click `Create By Connecting To An External Database`, you need to specify the project name, API type, and other database parameters.
Tip 1: If you are running NocoDB on Docker and your local DB is running on your host machine, your Host Address would be host.docker.internal instead of localhost.
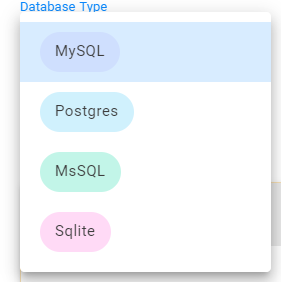
Currently it supports MySQL, Postgres, MSSQL and SQLite.
You can also configure associated SSL & advanced parameters.
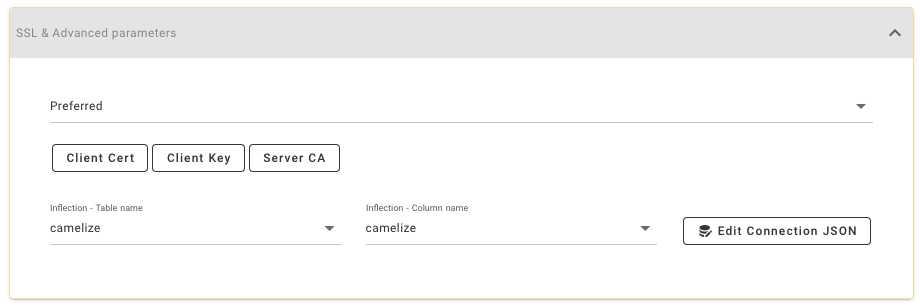
Tip 2: You can click Edit Connection JSON and modify SSL settings in "ssl".
```json
{
"client": "pg",
"connection": {
"host": "",
"port": "5432",
"user": "",
"password": "",
"database": "",
"ssl": {
"require": true,
"rejectUnauthorized": false,
"sslMode": "no-verify"
}
}
}
```
Tip 3: You can click Edit Connection JSON and specify the schema you want to use in "searchPath".
```json
{
"client": "pg",
"connection": {
...
},
"searchPath": [ "" ]
}
```
Click `Test Database Connection` to see if the connection can be established or not. NocoDB creates a new **empty database** with specified parameters if the database doesn't exist.