mirror of https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb
80 changed files with 667 additions and 1277 deletions
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
||||
NC_INSTALL_ROOT=./ |
||||
NO_COLOR=NEST_JS_LOG_MESSAGE_NO_COLOR_SET_NON_NULL_VALUE |
||||
@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Install all-in-one nocodb with Docker (compose) |
||||
|
||||
This page provides instructions to install nocodb all-in-one (aio) using Docker-Compse. The installation will run multiple contianers in single node which includes |
||||
- nocodb |
||||
- postgres |
||||
- nginx |
||||
- redis |
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
Before you begin, ensure you have the following prerequisites: |
||||
|
||||
- Docker (version 20.10.7 or later) |
||||
- Docker-Compose (version 2.17.3 or later) |
||||
- Ports 80 and 443 are available |
||||
|
||||
TIP: you could simply run [./pre-req-check.sh](./pre-req-check.sh) which performs pre-requisite check. |
||||
|
||||
## Install |
||||
Run [install.sh](./install.sh), This script performs pre-requisite check, prompts you through required application properties and finally performs `docker-compose up -d`. |
||||
For most cases where no external integration required. The defaults properties are just fine. |
||||
``` |
||||
sudo ./install.sh |
||||
``` |
||||
Note: sudo is required for docker to run unless you have configured docker user to be part of sudoers. If sudo is not used then you will get error `('Connection aborted.', PermissionError(13, 'Permission denied'))` |
||||
|
||||
* At this point, your installation is completed and you should be able to access your nocodb instance * |
||||
|
||||
### An example output will be like below. |
||||
``` |
||||
./install.sh |
||||
** Performing nocodb system check and setup. This step may require sudo permissions |
||||
| Checking if required tools (docker, docker-compose, jq, lsof) are installed... |
||||
| Checking port accessibility... |
||||
| Port 80 is free. |
||||
| WARNING: Port 443 is in use. Please make sure it is free. |
||||
** System check completed successfully. ** |
||||
** Few pre-requisites are failing. Recommend to resolve and proceed. However you could still proceed to install ** |
||||
| Press Y to continue or N to skip (Y/N)? |
||||
Preparing environment file before install.. |
||||
| Press Y to continue with defaults or N to customise app properties (Y/N) |
||||
Backing up previous docker-compose/aio/conf/nc_properties.env file to nocodb/docker-compose/aio/conf/nc_properties.env-1707455571.bak |
||||
Environment variables written to docker-compose/aio/conf/nc_properties.env file. |
||||
Installing docker containers |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
## Data and Conf directories |
||||
This directory acts as the NC_INSTALL_ROOT by default and it will have data, conf directories which are `.gitingore` to avoid accidentlly exposing to git repository. |
||||
During installation the default properties are configured at [nc_properties.env](./conf/nc_properties.env) which can be updated if required and restarted |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
. |
||||
├── conf |
||||
│ └── nc_properties.env |
||||
├── data |
||||
│ ├── nginx |
||||
│ ├── nocodb |
||||
│ ├── postgres |
||||
│ └── redis |
||||
├── docker |
||||
│ └── docker-compose.yml |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## what does install.sh do |
||||
[Install script](./install.sh) performs the following steps |
||||
1. pre-req-check.sh and warns if there is anything missing which could potentially cause issues at later stage. However it will let you proceed if you wish to. |
||||
2. create application properties file under conf dir which will then be used for future upgrades etc. |
||||
3. runs docker-compose up -d |
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Operations |
||||
Refer [advanced section](./advanced.md) for advanced operations like setting up ssl, updating configurations, restarts etc |
||||
@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Advanced operations |
||||
|
||||
## Restarting containers |
||||
There are atleast 4 main containers which are running as part of this installation through same docker-compose. The same docker-compose can be leveraged to restart any or all of these containers. |
||||
|
||||
Use [restart.sh](./bin/restart.sh) or Use below command to restart all containers |
||||
``` docker compose restart ``` |
||||
|
||||
To restart individual containers with name ( names: nocodb, nginx, postgres, redis)\ |
||||
ex: to restart nginx\ |
||||
``` docker compose restart nginx ``` |
||||
|
||||
## Reload nginx |
||||
use utility script at [./bin/nginx_reload.sh](./bin/nginx_reload.sh) |
||||
|
||||
## [TBD] Upgrade nocodb instance |
||||
|
||||
## Enable SSL |
||||
To enable SSL for incoming https requests, nginx should be configured with combination of a public certificate and a private key. The SSL private key is kept secret on the server. It will be used to encrypt content sent to clients. |
||||
Below are different approaches to get and configure certificates. Make your choice |
||||
### letsencrypt for generating certificates |
||||
Certificates/key can be obtained by trusted CA (Certificate Authorities), there are many paid vendors found online or you can also use [letsencrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/) a non profit certificate provider for free however we recommend [donating](https://www.abetterinternet.org/donate/) for their work. |
||||
|
||||
Run the script to create certificate using the script |
||||
``` |
||||
./bin/gen_letsencrypt_cert.sh |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### [TBD] Bring your own certificates |
||||
If you already have the certificates, either self signed or generated by any other means, you will need to configure them with nginx. Below are the steps |
||||
|
||||
### [TBD] Self signed certificates |
||||
One of the pre-requisite is that your server should be associated with the domain name. In the absence of that you could use self signed certificates which does ecrypt but browsers show warning. |
||||
|
||||
## Database password rotation |
||||
As a security measure, It is best practice to rotate the database credentials periodically. Assuming you would have created new credentials in postgres database. The db credentials are persisted on filesystem as part of initial install and it will be available at |
||||
[./conf/nc_properties.env](./conf/nc_properties.env)\ |
||||
update properties POSTGRES_USER, POSTGRES_PASSWORD with new credentials and [restarting nocodb](#restarting-containers) with\ |
||||
```docker compose restart nocodb``` |
||||
|
||||
## nginx configurations |
||||
There are two main directories where nginx configurations are maintained |
||||
- nocodb team managed configurations at [nginx/conf.d](./conf/nginx/conf.d). |
||||
- self managed (you) [conf/nginx/conf.d](./conf/nginx/conf.d) |
||||
|
||||
## postgres configurations |
||||
[postgres.conf](./data/postgres/postgresql.conf) and [pg_hba.conf](./data/postgres/pg_hba.conf) are created under ./data/postgres directory upon first postgres container creation. The configurations can be updated and restarted continer to take affect. |
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# expects nginx to be up and running with conf.d/certbot.conf |
||||
# dns to be mapped to the machine where cert is generated |
||||
# |
||||
|
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
|
||||
SERVER_NAME=${1} |
||||
if [[ -z "$SERVER_NAME" ]] |
||||
then |
||||
echo "required argument servername" |
||||
echo "usage ex: ./gen_certs my.nocodb.com" |
||||
exit 1 |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
echo "Creating configs for SERVER_NAME: ${SERVER_NAME}" |
||||
cd ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../conf/nginx/conf.d |
||||
sed "s,<SERVER_NAME>,${SERVER_NAME},g" ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../nginx/conf-templates/certbot_conf.template > certbot.conf |
||||
|
||||
cd ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../bin |
||||
./nginx_start.sh |
||||
./nginx_reload.sh |
||||
|
||||
echo "Triggering certbot to create ssl configs: ${SERVER_NAME}" |
||||
cd ${SCRIPT_DIR}/.. |
||||
docker-compose run --rm certbot certonly --webroot --webroot-path /var/www/certbot/ -d ${SERVER_NAME} |
||||
result=$? |
||||
|
||||
if [[ $result == 1 ]]; then |
||||
echo "cert generation failed" |
||||
echo "rolling back the certs and reloading nginx" |
||||
else |
||||
echo "Now reload nginx with new ssl configs for your site : ${SERVER_NAME}" |
||||
cd ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../conf/nginx/conf.d |
||||
rm -f certbot.conf |
||||
sed "s,<SERVER_NAME>,${SERVER_NAME},g" ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../nginx/conf-templates/ssl_server_name_conf.template > ${SERVER_NAME}.conf |
||||
fi |
||||
rm -rf ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../conf/nginx/conf.d/certbot.conf |
||||
${SCRIPT_DIR}/../bin/nginx_reload.sh |
||||
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
docker exec -it nginx /etc/init.d/nginx reload |
||||
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# starts the docker containers configured in this components |
||||
# docker compose dir |
||||
# |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
|
||||
COMPONENT_DIR=${SCRIPT_DIR}/../ |
||||
cd ${COMPONENT_DIR} |
||||
mkdir -p ${COMPONENT_DIR}/data |
||||
chmod -R 777 ${COMPONENT_DIR}/data |
||||
docker-compose restart nginx |
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
cd ${SCRIPT_DIR}/../ |
||||
sudo docker-compose run --rm certbot renew -q |
||||
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# docker-compose restart all containers utilty script |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
|
||||
COMPONENT_DIR=${SCRIPT_DIR}/../ |
||||
cd ${COMPONENT_DIR} |
||||
docker-compose restart |
||||
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# docker-compose start |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
|
||||
COMPONENT_DIR=${SCRIPT_DIR}/../ |
||||
cd ${COMPONENT_DIR} |
||||
docker-compose up -d |
||||
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Environment Variables |
||||
POSTGRES_USER=postgres |
||||
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=test123 |
||||
POSTGRES_DB=nocodb |
||||
NC_REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379/4 |
||||
NC_DB=pg://postgres:5432?u=postgres&password=${POSTGRES_PASSWORD:-nocodb}&d=postgres |
||||
NC_PUBLIC_URL=http://rajanishs-MacBook-Pro.local |
||||
NC_CONNECT_TO_EXTERNAL_DB_DISABLED=false |
||||
NC_INVITE_ONLY_SIGNUP=false |
||||
NC_ADMIN_EMAIL=admin@nocodb.com |
||||
NC_ADMIN_PASSWORD=nocodb123 |
||||
NC_S3_BUCKET_NAME=nocodb-attachements |
||||
|
||||
@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
version: '3.8' |
||||
|
||||
networks: |
||||
nocodb-001: |
||||
# external: true |
||||
|
||||
services: |
||||
redis: |
||||
image: redis:latest |
||||
container_name: redis |
||||
restart: unless-stopped |
||||
env_file: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nc_properties.env |
||||
expose: |
||||
- "6379" |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/data/redis:/data |
||||
networks: |
||||
- nocodb-001 |
||||
deploy: |
||||
resources: |
||||
limits: |
||||
cpus: '0.5' |
||||
memory: 1000M |
||||
|
||||
postgres: |
||||
image: postgres:14.7 |
||||
container_name: postgres |
||||
restart: unless-stopped |
||||
env_file: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nc_properties.env |
||||
expose: |
||||
- "5432" |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/data/postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data |
||||
networks: |
||||
- nocodb-001 |
||||
healthcheck: |
||||
interval: 10s |
||||
retries: 10 |
||||
test: "pg_isready -U ${POSTGRES_USER} -d ${POSTGRES_DB}" |
||||
timeout: 2s |
||||
deploy: |
||||
resources: |
||||
limits: |
||||
cpus: '1' |
||||
memory: 1000M |
||||
|
||||
nocodb: |
||||
depends_on: |
||||
- postgres |
||||
- redis |
||||
image: nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
container_name: nocodb |
||||
restart: unless-stopped |
||||
env_file: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nc_properties.env |
||||
expose: |
||||
- "8080" |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/data/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ |
||||
networks: |
||||
- nocodb-001 |
||||
deploy: |
||||
resources: |
||||
limits: |
||||
cpus: '1' |
||||
memory: 1000M |
||||
|
||||
nginx: |
||||
container_name: nginx |
||||
depends_on: |
||||
- nocodb |
||||
image: nginx |
||||
restart: unless-stopped |
||||
env_file: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nc_properties.env |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d:ro |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/custom-conf.d:ro |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/nginx/conf:/opt/nocohub/nginx/conf |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/data/nginx:/opt/nocohub/nginx/data |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nginx/certbot/www:/var/www/certbot/:ro |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nginx/certbot/conf/:/etc/nginx/ssl/:ro |
||||
# - ../nginx/conf/ssl:/etc/nginx/ssl/:ro |
||||
expose: |
||||
- "80" |
||||
- "443" |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "80:80" |
||||
- "443:443" |
||||
networks: |
||||
- nocodb-001 |
||||
deploy: |
||||
resources: |
||||
limits: |
||||
cpus: '1' |
||||
memory: 1000M |
||||
certbot: |
||||
container_name: nocodb_certbot |
||||
image: certbot/certbot:latest |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nginx/certbot/www:/var/www/certbot/:rw |
||||
- ${NC_INSTALL_ROOT:-/opt/nocodb}/conf/nginx/certbot/conf/:/etc/letsencrypt/:rw |
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# Performs Initial setup and System Requirements Check |
||||
|
||||
## 1. validate system requirements |
||||
# a. docker, docker-compose, jq installed |
||||
# b. port mapping check |
||||
# - port 80,443 are free or being used by nginx container |
||||
# - port 8080 is open if used for multi-instance setup |
||||
# - port 6379 for redis access |
||||
# - port 9001 for minio access |
||||
# c. docker repo accessiblity quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2023-12-09T18-17-51Z, redis:latest, postgres:14.7, nocodb/nocodb:latest, nginx |
||||
# d. licence check (tbd) |
||||
|
||||
# -- main line code starts here |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
## utility functions |
||||
source ${SCRIPT_DIR}/sbin/util.sh |
||||
|
||||
${SCRIPT_DIR}/pre-req-check.sh |
||||
PRE_REQ_SUCCESS=$? |
||||
if [[ ${PRE_REQ_SUCCESS} != 0 ]] |
||||
then |
||||
echo "** Few pre-requisites are failing. Recommend to resolve and proceed. However you could still proceed to install **" >&2 |
||||
else |
||||
echo "** All pre-requistites are taken care of. Proceeding to install.. **" |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
# ask do you want to proceed with all defaults, |
||||
# if yes, then no prompts |
||||
if asksure; then |
||||
echo "Preparing environment file before install.." |
||||
promptUser=true |
||||
if asksure " | Press Y to continue with defaults or N to customise app properties (Y/N)"; then |
||||
promptUser=false |
||||
fi |
||||
${SCRIPT_DIR}/prepare_env.sh ${promptUser} |
||||
echo "Installing docker containers" |
||||
docker-compose -f ${SCRIPT_DIR}/docker-compose.yml up -d |
||||
else |
||||
echo "Exiting without install. You can install using docker-compose -f ${SCRIPT_DIR}/docker-compose.yml up -d " |
||||
fi |
||||
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
server { |
||||
listen 80; |
||||
listen [::]:80; |
||||
|
||||
# chantge server_name while generating cert |
||||
server_name <SERVER_NAME>; |
||||
|
||||
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main; |
||||
|
||||
# this is required for cert generation. |
||||
# change server_name as well with cname of required cert |
||||
location /.well-known/acme-challenge/ { |
||||
root /var/www/certbot; |
||||
} |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
server { |
||||
listen 443 default_server ssl; |
||||
listen [::]:443 ssl ; |
||||
# chantge server_name while generating cert |
||||
server_name <SERVER_NAME>; |
||||
|
||||
# force https-redirects |
||||
if ($scheme = http) { |
||||
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri; |
||||
} |
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/live/<SERVER_NAME>/fullchain.pem; |
||||
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/live/<SERVER_NAME>/privkey.pem; |
||||
|
||||
location / { |
||||
proxy_pass http://nocodb_backend; |
||||
proxy_set_header Host $host; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; |
||||
proxy_http_version 1.1; |
||||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; |
||||
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; |
||||
proxy_intercept_errors on; |
||||
} |
||||
|
||||
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root |
||||
# concurs with nginx's one |
||||
# |
||||
location ~ /\.ht { |
||||
deny all; |
||||
} |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
upstream nocodb_backend { |
||||
server nocodb:8080; |
||||
# server nocodb-1:8080; |
||||
# server nocodb-2:8080; |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
server { |
||||
|
||||
listen 80; |
||||
listen [::]:80; |
||||
server_name localhost; |
||||
|
||||
location / { |
||||
proxy_pass http://nocodb_backend; |
||||
proxy_set_header Host $host; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; |
||||
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; |
||||
proxy_http_version 1.1; |
||||
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; |
||||
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; |
||||
proxy_intercept_errors on; |
||||
error_page 404 = @handle404; |
||||
} |
||||
|
||||
location @handle404 { |
||||
rewrite ^ /dashboard permanent; |
||||
} |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
||||
events { |
||||
worker_connections 1024; |
||||
} |
||||
|
||||
http { |
||||
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; |
||||
include /etc/nginx/custom-conf.d/*.conf; |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# Performs Initial setup and System Requirements Check |
||||
|
||||
## 1. validate system requirements |
||||
# a. docker, docker-compose, jq installed |
||||
# b. port mapping check |
||||
# - port 80,443 are free or being used by nginx container |
||||
# - port 8080 is open if used for multi-instance setup |
||||
# - port 6379 for redis access |
||||
# - port 9001 for minio access |
||||
# c. docker repo accessiblity quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2023-12-09T18-17-51Z, redis:latest, postgres:14.7, nocodb/nocodb:latest, nginx |
||||
# d. licence check (tbd) |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- main line code starts here |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
source ${SCRIPT_DIR}/sbin/util.sh |
||||
source ${SCRIPT_DIR}/sbin/install_vars.sh |
||||
echo "** Performing nocodb system check and setup. This step may require sudo permissions" |
||||
PRE_REQ=0 |
||||
|
||||
# d. Check if required tools are installed |
||||
echo " | Checking if required tools (docker, docker-compose, jq, lsof) are installed..." |
||||
for tool in docker docker-compose lsof; do |
||||
if ! command -v "$tool" &> /dev/null; then |
||||
echo " | Error: $tool is not installed. Please install it before proceeding." |
||||
PRE_REQ=1 |
||||
fi |
||||
done |
||||
|
||||
# e. Check if NocoDB is already installed and its expected version |
||||
# echo "Checking if NocoDB is already installed and its expected version..." |
||||
# Replace the following command with the actual command to check NocoDB installation and version |
||||
# Example: nocodb_version=$(command_to_get_nocodb_version) |
||||
# echo "NocoDB version: $nocodb_install_version" |
||||
|
||||
# f. Port mapping check |
||||
echo " | Checking port accessibility..." |
||||
for port in "${REQUIRED_PORTS[@]}"; do |
||||
if lsof -Pi :$port -sTCP:LISTEN -t >/dev/null; then |
||||
echo " | WARNING: Port $port is in use. Please make sure it is free." >&2 |
||||
PRE_REQ=1 |
||||
else |
||||
echo " | Port $port is free." |
||||
fi |
||||
done |
||||
|
||||
# # g. Docker repository accessibility check |
||||
# echo "Checking Docker repository accessibility..." |
||||
# for image in "${DOCKER_IMAGES[@]}"; do |
||||
# if docker pull "$image" &> /dev/null; then |
||||
# echo "Docker image $image is accessible." |
||||
# else |
||||
# echo "Error: Docker image $image is not accessible. Please check the repository or internet connection." |
||||
# PRE_REQ=1 |
||||
# fi |
||||
# done |
||||
|
||||
echo "** System check completed successfully. **" |
||||
exit $PRE_REQ |
||||
@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# prepares env file with all the required env variables. |
||||
# |
||||
|
||||
# -- main line code starts here -- |
||||
SCRIPT_DIR=$( cd -- "$( dirname -- "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" &> /dev/null && pwd ) |
||||
source ${SCRIPT_DIR}/sbin/util.sh |
||||
source ${SCRIPT_DIR}/sbin/install_vars.sh |
||||
|
||||
ENV_FILE=${SCRIPT_DIR}/conf/nc_properties.env |
||||
bkp_file=${ENV_FILE}-$(date +%s).bak |
||||
# Source existing nc_envs.env file to get current values |
||||
if [ -f ${ENV_FILE} ]; then |
||||
source ${ENV_FILE} |
||||
echo "Backing up previous ${ENV_FILE} file to ${bkp_file}" |
||||
cp ${ENV_FILE} ${bkp_file} |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
function trim(){ |
||||
local var="${@}" |
||||
echo "$(sed -e 's/[[:space:]]*$//' <<<${var})" |
||||
} |
||||
|
||||
function acceptProperty(){ |
||||
local varDetail="$1" |
||||
local promptUser="${2:-true}" |
||||
prompt=$(echo "$varDetail" | cut -d '|' -f2) |
||||
prop=$(echo "$varDetail" | cut -d '|' -f1) |
||||
key=$(echo "$prop" | cut -d'=' -f1) |
||||
default_value="${prop#*=}" |
||||
prev_value_or_default=${!key:-${default_value}} |
||||
|
||||
# echo promptUser: ${promptUser} |
||||
# echo prop: ${prop} |
||||
# echo key: ${key} |
||||
# echo default_value: ${default_value} |
||||
if [[ ${promptUser} == "true" ]]; then |
||||
read -p " || Enter value for $key (default: ${prev_value_or_default}): " user_input |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
# Use user input or default value if empty |
||||
value=$(trim ${user_input:-$prev_value_or_default}) |
||||
|
||||
# Store key-value pair in a variable |
||||
if [[ ${value} != "" ]]; then |
||||
userValues="${userValues}${key}=${value}\n" |
||||
fi |
||||
} |
||||
# Iterate over the properties array and prompt user for input |
||||
for multi_property_array in basic_properties invite_only_signup_priorities google_login_properties email_properties s3_attachment_properties ; do |
||||
array_name="$multi_property_array[@]" # Name of the array to process |
||||
array=("${!array_name}") |
||||
promptUser="${1}" |
||||
for varDetail in "${array[@]}"; do |
||||
promptMsg=$(echo "$varDetail" | cut -d '|' -f2) |
||||
prop=$(echo "$varDetail" | cut -d '|' -f1) |
||||
if [[ ${promptUser} == "true" ]] && [[ ${prop} == "main" ]] |
||||
then |
||||
echo $promptMsg |
||||
if ! asksure; then |
||||
# set all defaults here |
||||
promptUser=false |
||||
fi |
||||
continue |
||||
fi |
||||
if [[ ${prop} != "main" ]]; then |
||||
acceptProperty "${varDetail}" "${promptUser}" |
||||
fi |
||||
done |
||||
done |
||||
|
||||
# Write key-value pairs to nc_envs.env file |
||||
echo -e "# Environment Variables\n$userValues" > ${ENV_FILE} |
||||
|
||||
echo "Environment variables written to ${ENV_FILE} file." |
||||
|
||||
# echo "creating data conf, data and log directories" |
||||
# mkdir -p ${INSTALL_ROOT}/conf ${INSTALL_ROOT}/data ${INSTALL_ROOT}/logs |
||||
@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
|
||||
nocodb_install_version="1.0.0" # Replace with actual version |
||||
REQUIRED_PORTS=(80 443) |
||||
DOCKER_IMAGES=("redis:latest" "postgres:14.7" "nocodb/nocodb:latest" "nginx" "certbot/certbot:latest" ) |
||||
|
||||
# Array of properties with default values |
||||
basic_properties=( |
||||
"main|Basic Configurations" |
||||
"POSTGRES_USER=postgres | Username for postgres database" |
||||
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD=test123 | " |
||||
"POSTGRES_DB=nocodb | " |
||||
"NC_REDIS_URL=redis://redis:6379/4 | default to redis container" |
||||
'NC_DB=pg://postgres:5432?u=postgres&password=${POSTGRES_PASSWORD:-nocodb}&d=postgres | hide' |
||||
"NC_PUBLIC_URL=http://$(hostname) | Are you using custom DNS, configure NC_PUBLIC_URL to reflect in the invite emails?" |
||||
"NC_CONNECT_TO_EXTERNAL_DB_DISABLED=false | Disable connecting to external db?" |
||||
) |
||||
|
||||
invite_only_signup_priorities=( |
||||
"main|Allow invite only sign-up" |
||||
"NC_INVITE_ONLY_SIGNUP=false | invite only signup?" |
||||
"NC_ADMIN_EMAIL=admin@nocodb.com | " |
||||
"NC_ADMIN_PASSWORD=nocodb123 | " |
||||
) |
||||
|
||||
google_login_properties=( |
||||
"main|Configure Google Login" |
||||
"NC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID= | Enter Client ID" |
||||
"NC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET= | Enter Client ID") |
||||
|
||||
email_properties=( |
||||
"main|Configure smtp properties" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_FROM= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_HOST= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_PORT= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_USERNAME= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_PASSWORD= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_SECURE= |" |
||||
"NC_SMTP_IGNORE_TLS= |" |
||||
) |
||||
|
||||
s3_attachment_properties=( |
||||
"main|Do you want to configure s3 for attachements?" |
||||
"NC_S3_BUCKET_NAME=nocodb-attachements |" |
||||
"NC_S3_REGION= |" |
||||
"NC_S3_ACCESS_KEY= | " |
||||
"NC_S3_ACCESS_SECRET= |" |
||||
) |
||||
|
||||
multi_property_array=(basic_properties invite_only_signup_priorities google_login_properties email_properties s3_attachment_properties) |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
|
||||
echo "install docker and compose" |
||||
sudo apt update |
||||
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings |
||||
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg |
||||
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt update |
||||
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common -y |
||||
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg |
||||
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null |
||||
sudo apt update |
||||
apt-cache policy docker-ce |
||||
sudo apt install docker-ce -y |
||||
sudo apt install docker-compose -y |
||||
apt-get install jq -y |
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash |
||||
# this file contains the utility functions |
||||
# used during installation |
||||
# |
||||
|
||||
asksure() { |
||||
local custom_msg="${@}" |
||||
if [[ ${custom_msg} ]]; then |
||||
echo -n "${custom_msg}" |
||||
else |
||||
echo -n " | Press Y to continue or N to skip (Y/N)? " |
||||
fi |
||||
while read -r -n 1 -s answer; do |
||||
if [[ $answer = [YyNn] ]]; then |
||||
[[ $answer = [Yy] ]] && retval=0 |
||||
[[ $answer = [Nn] ]] && retval=1 |
||||
break |
||||
fi |
||||
done |
||||
|
||||
echo # just a final linefeed, optics... |
||||
|
||||
return $retval |
||||
} |
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
read -p "Enter your domain name: " domain |
||||
read -p "Enter your email id: " email |
||||
|
||||
# Docker installation |
||||
if [ -x "$(command -v docker)" ]; then |
||||
echo "Docker already available" |
||||
else |
||||
sudo apt-get update |
||||
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg2 software-properties-common |
||||
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo apt-key add -- |
||||
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian buster stable" |
||||
sudo apt-get update |
||||
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io |
||||
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER |
||||
echo "Docker installed successfully" |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
# Docker compose installation |
||||
if [ -x "$(command -v docker-compose)" ]; then |
||||
echo "Docker-compose already available" |
||||
else |
||||
sudo apt-get -y install wget |
||||
sudo wget https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.26.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m) -O /usr/local/bin/docker-compose |
||||
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose |
||||
docker-compose --version |
||||
echo "Docker-compose installed successfully" |
||||
fi |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#wget https://github.com/evertramos/docker-compose-letsencrypt-nginx-proxy-companion/archive/master.zip -O master.zip |
||||
# |
||||
#unzip -n master.zip |
||||
# |
||||
#cd docker-compose-letsencrypt-nginx-proxy-companion-master |
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/evertramos/docker-compose-letsencrypt-nginx-proxy-companion.git |
||||
|
||||
cd docker-compose-letsencrypt-nginx-proxy-companion |
||||
|
||||
OUTPUT1=$(./start.sh) |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 8081:8081 -p 8082:8082 -d --name xc-instant \ |
||||
-e VIRTUAL_HOST="$domain" \ |
||||
-e LETSENCRYPT_HOST="$domain" \ |
||||
-e LETSENCRYPT_EMAIL="$email" \ |
||||
-e VIRTUAL_PORT=8080 \ |
||||
--network=webproxy nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
version: "2.1" |
||||
services: |
||||
nocodb: |
||||
depends_on: |
||||
root_db: |
||||
condition: service_healthy |
||||
environment: |
||||
NC_DB: "mysql2://root_db:3306?u=noco&p=password&d=root_db" |
||||
image: "nocodb/nocodb:latest" |
||||
ports: |
||||
- "8080:8080" |
||||
restart: always |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- "nc_data:/usr/app/data" |
||||
root_db: |
||||
environment: |
||||
MYSQL_DATABASE: root_db |
||||
MYSQL_PASSWORD: password |
||||
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: password |
||||
MYSQL_USER: noco |
||||
healthcheck: |
||||
retries: 10 |
||||
test: |
||||
- CMD |
||||
- mysqladmin |
||||
- ping |
||||
- "-h" |
||||
- localhost |
||||
timeout: 20s |
||||
image: "mysql:8.3.0" |
||||
restart: always |
||||
volumes: |
||||
- "db_data:/var/lib/mysql" |
||||
# below line shows how to change charset and collation |
||||
# uncomment it if necessary |
||||
# command: --character-set-server=utf8mb4 --collation-server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci |
||||
volumes: |
||||
db_data: {} |
||||
nc_data: {} |
||||
Binary file not shown.
@ -1,410 +0,0 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Installation' |
||||
description: 'Simple installation - takes about three minutes!' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB docker installation', 'NocoDB nodejs installation', 'NocoDB quick try', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
Simple installation - takes about three minutes! |
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
- [Docker](https://www.docker.com/get-started) or [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/download) ( > v18.x ) |
||||
|
||||
## Quick try |
||||
|
||||
### Docker |
||||
|
||||
If you are a Docker user, you may try this way! |
||||
|
||||
<Tabs> |
||||
<TabItem value="sqlite" label="SQLite"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker run -d --name nocodb \ |
||||
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \ |
||||
-p 8080:8080 \ |
||||
nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="postgres" label="Postgres"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker run -d --name nocodb-postgres \ |
||||
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \ |
||||
-p 8080:8080 \ |
||||
-e NC_DB="pg://host.docker.internal:5432?u=root&p=password&d=d1" \ |
||||
-e NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET="569a1821-0a93-45e8-87ab-eb857f20a010" \ |
||||
nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
</Tabs> |
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
To persist data in docker you can mount volume at `/usr/app/data/` since 0.10.6. In older version mount at `/usr/src/app`. Otherwise your data will be lost after recreating the container. |
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Compose |
||||
|
||||
We provide different docker-compose.yml files under [this directory](https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb/tree/master/docker-compose). Here are some examples. |
||||
|
||||
<Tabs> |
||||
<TabItem value="postgres" label="Postgres"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb |
||||
cd nocodb/docker-compose/pg |
||||
docker-compose up -d |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
</Tabs> |
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
If `/usr/app/data/` is not mounted, there will be data loss. |
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Homebrew |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
brew tap nocodb/nocodb |
||||
brew install nocodb |
||||
nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
### Executables |
||||
|
||||
You can download executables directly and run without any extra dependency. Use the right command based on your platform. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs> |
||||
<TabItem value="MacOS (x64)" label="MacOS (x64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
curl http://get.nocodb.com/macos-x64 -o nocodb -L \ |
||||
&& chmod +x nocodb \ |
||||
&& ./nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
<TabItem value="MacOS (arm64)" label="MacOS (arm64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
curl http://get.nocodb.com/macos-arm64 -o nocodb -L \ |
||||
&& chmod +x nocodb \ |
||||
&& ./nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
<TabItem value="Linux (x64)" label="Linux (x64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
curl http://get.nocodb.com/linux-x64 -o nocodb -L \ |
||||
&& chmod +x nocodb \ |
||||
&& ./nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
<TabItem value="Linux (arm64)" label="Linux (arm64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
curl http://get.nocodb.com/linux-arm64 -o nocodb -L \ |
||||
&& chmod +x nocodb \ |
||||
&& ./nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
<TabItem value="Windows (x64)" label="Windows (x64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
iwr http://get.nocodb.com/win-x64.exe -OutFile "Noco-win-x64.exe" |
||||
.\Noco-win-x64.exe |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
<TabItem value="Windows (arm64)" label="Windows (arm64)"> |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
iwr http://get.nocodb.com/win-arm64.exe -OutFile "Noco-win-arm64.exe" |
||||
.\Noco-win-arm64.exe |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
</Tabs> |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Node Application |
||||
|
||||
We provide a simple NodeJS Application for getting started. |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb-seed |
||||
cd nocodb-seed |
||||
npm install |
||||
npm start |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### AWS ECS (Fargate) |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Create ECS Cluster |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
aws ecs create-cluster \ |
||||
--cluster-name <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
#### Create Log group |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
aws logs create-log-group \ |
||||
--log-group-name /ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
#### Create ECS Task Definiton |
||||
|
||||
Every time you create it, it will add a new version. If it is not existing, the version will be 1. |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
aws ecs register-task-definition \ |
||||
--cli-input-json "file://./<YOUR_TASK_DEF_NAME>.json" |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
This json file defines the container specification. You can define secrets such as NC_DB and environment variables here. |
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
Here's the sample Task Definition |
||||
|
||||
```json |
||||
{ |
||||
"family": "nocodb-sample-task-def", |
||||
"networkMode": "awsvpc", |
||||
"containerDefinitions": [{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>", |
||||
"image": "nocodb/nocodb:latest", |
||||
"essential": true, |
||||
"logConfiguration": { |
||||
"logDriver": "awslogs", |
||||
"options": { |
||||
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>", |
||||
"awslogs-region": "<YOUR_AWS_REGION>", |
||||
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs" |
||||
} |
||||
}, |
||||
"secrets": [{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_SECRETS_NAME>", |
||||
"valueFrom": "<YOUR_SECRET_ARN>" |
||||
}], |
||||
"environment": [{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME>", |
||||
"value": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_VALUE>" |
||||
}], |
||||
"portMappings": [{ |
||||
"containerPort": 8080, |
||||
"hostPort": 8080, |
||||
"protocol": "tcp" |
||||
}] |
||||
}], |
||||
"requiresCompatibilities": [ |
||||
"FARGATE" |
||||
], |
||||
"cpu": "256", |
||||
"memory": "512", |
||||
"executionRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_EXECUTION_ROLE_ARN>", |
||||
"taskRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_TASK_ROLE_ARN>" |
||||
} |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
#### Create ECS Service |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
aws ecs create-service \ |
||||
--cluster <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER> \ |
||||
--service-name <YOUR_SERVICE_NAME> \ |
||||
--task-definition <YOUR_TASK_DEF>:<YOUR_TASK_DEF_VERSION> \ |
||||
--desired-count <DESIRED_COUNT> \ |
||||
--launch-type "FARGATE" \ |
||||
--platform-version <VERSION> \ |
||||
--health-check-grace-period-seconds <GRACE_PERIOD_IN_SECOND> \ |
||||
--network-configuration "awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=["<YOUR_SUBSETS>"], securityGroups=["<YOUR_SECURITY_GROUPS>"], assignPublicIp=ENABLED}" \ |
||||
--load-balancer targetGroupArn=<TARGET_GROUP_ARN>,containerName=<CONTAINER_NAME>,containerPort=<YOUR_CONTAINER_PORT> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
|
||||
If your service fails to start, you may check the logs in ECS console or in Cloudwatch. Generally it fails due to the connection between ECS container and NC_DB. Make sure the security groups have the correct inbound and outbound rules. |
||||
|
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### GCP (Cloud Run) |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Pull NocoDB Image on Cloud Shell |
||||
|
||||
Since Cloud Run only supports images from Google Container Registry (GCR) or Artifact Registry, we need to pull NocoDB image, tag it and push it in GCP using Cloud Shell. Here are some sample commands which you can execute in Cloud Shell. |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
# pull latest NocoDB image |
||||
docker pull nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
|
||||
# tag the image |
||||
docker tag nocodb/nocodb:latest gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
|
||||
# push the image to GCR |
||||
docker push gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
#### Deploy NocoDB on Cloud Run |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
gcloud run deploy --image=gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest \ |
||||
--region=us-central1 \ |
||||
--allow-unauthenticated \ |
||||
--platform=managed |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### DigitalOcean (App) |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Create Apps |
||||
|
||||
On Home page, Click on Create icon & Select Apps (Deploy your code). |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Choose Source: Docker Hub |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Choose Source: Repository |
||||
|
||||
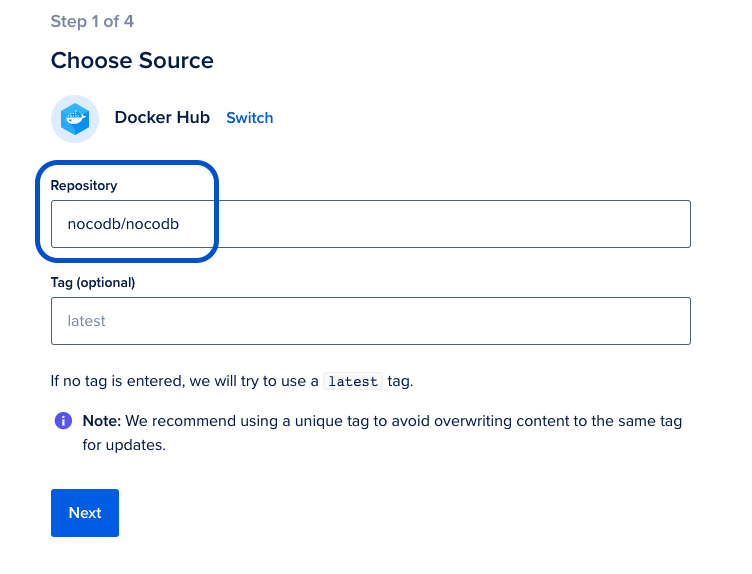
Configure Source Repository as `nocodb/nocodb`. Optionally you can pick release tag if you are interested in specific NocoDB version. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
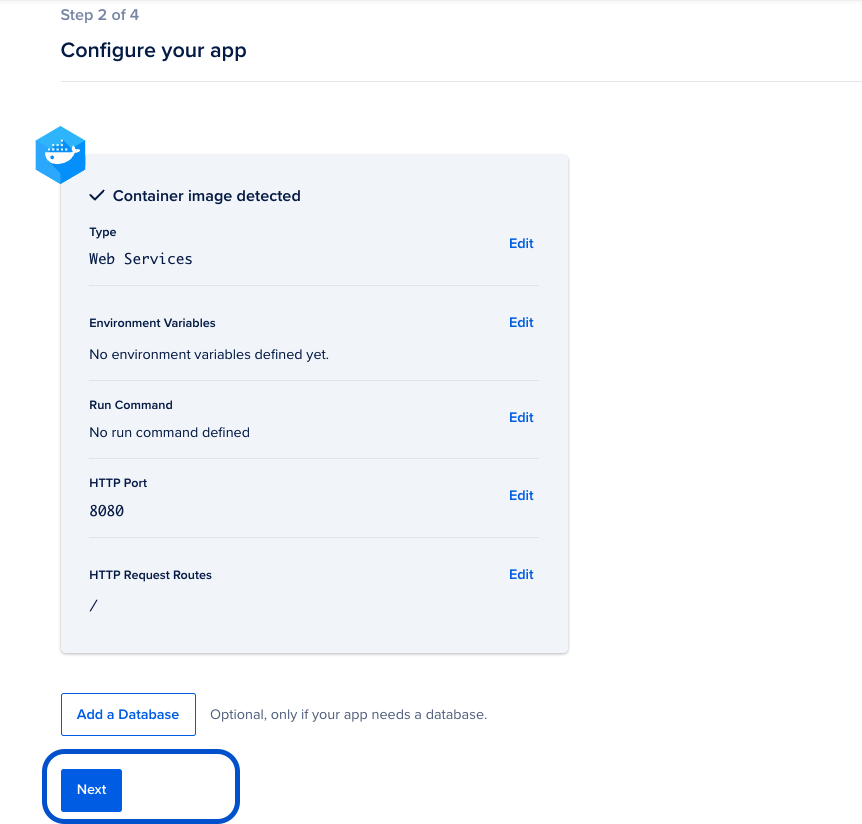
#### [Optional] Additional Configurations |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Name your web service |
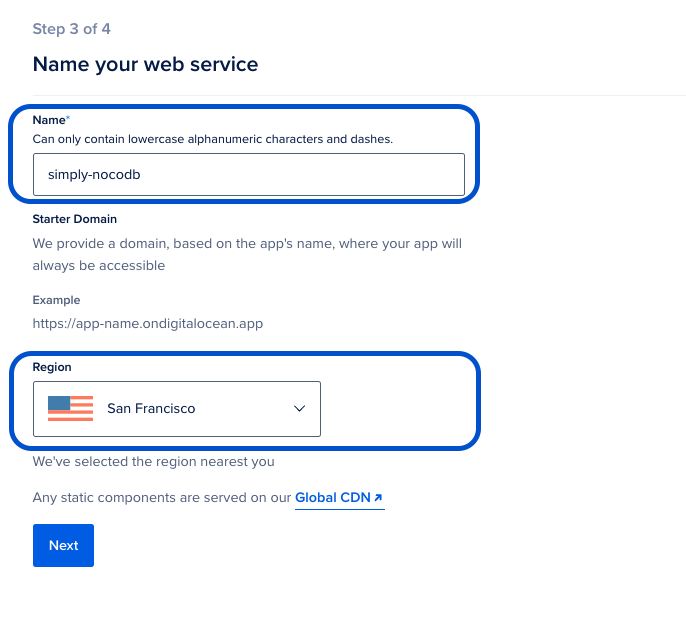
||||
Pick a name for your NocoDB application. This name will become part of URL subsequently |
||||
Pick nearest Region for cloud hosting |
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Finalize and Launch |
||||
|
||||
- Select hosting plan for your NocoDB application |
||||
|
||||
- Click "Launch APP" |
||||
|
||||
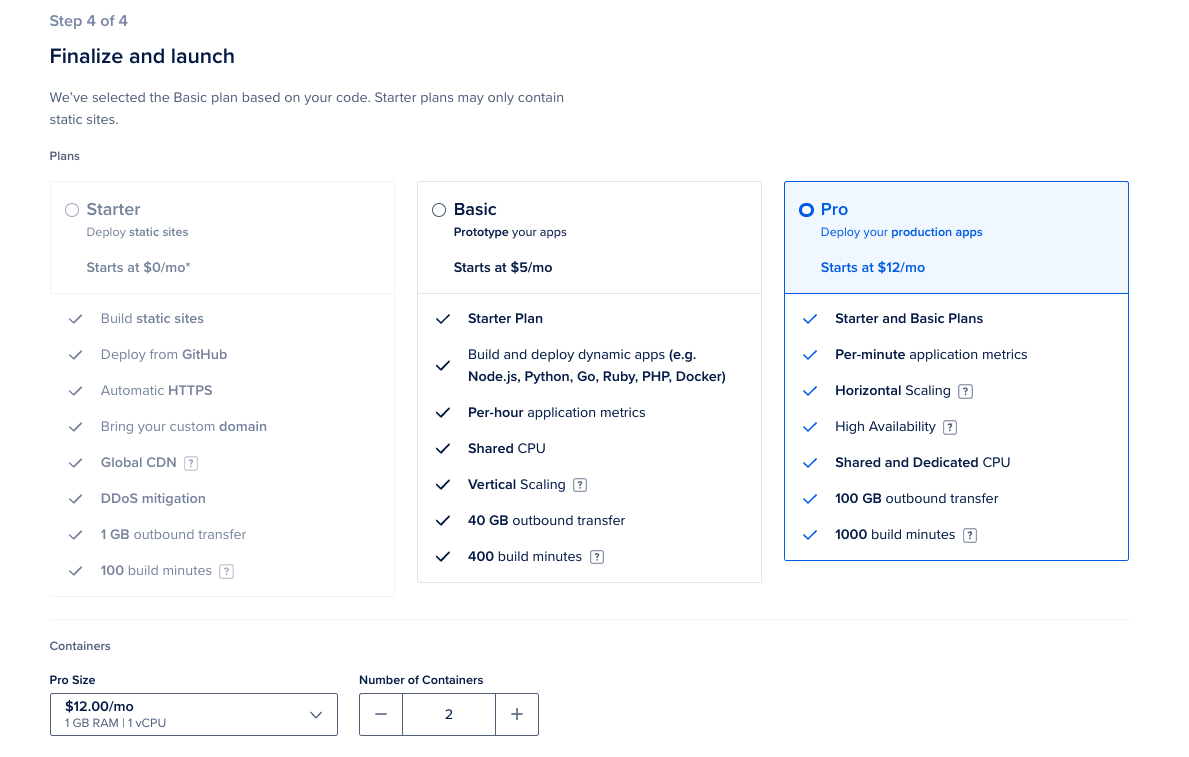 |
||||
|
||||
Application will be build & URL will be live in a minute! The URL will be something like https://simply-nocodb-rsyir.ondigitalocean.app/ |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### Cloudron |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Navigate to App Store |
||||
|
||||
Log into Cloudron and select App Store |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Search NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Click Install |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Configure NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
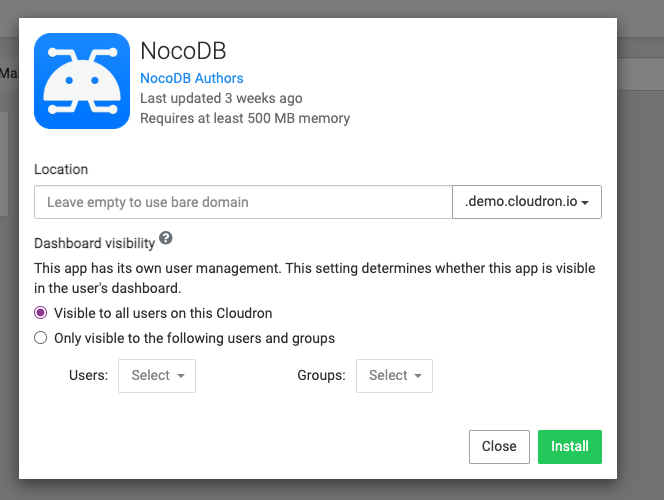 |
||||
|
||||
#### Go to My App and Launch NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### CapRover |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Login and Click One-Click Apps / Databases |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Search NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Configure NocoDB and Deploy |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### Railway |
||||
|
||||
<details> |
||||
<summary>Click to Expand</summary> |
||||
|
||||
#### Navigate to Templates |
||||
|
||||
Go to [Templates](https://railway.app/templates), Search NocoDB and click Deploy |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
#### Configure NocoDB and Deploy |
||||
|
||||
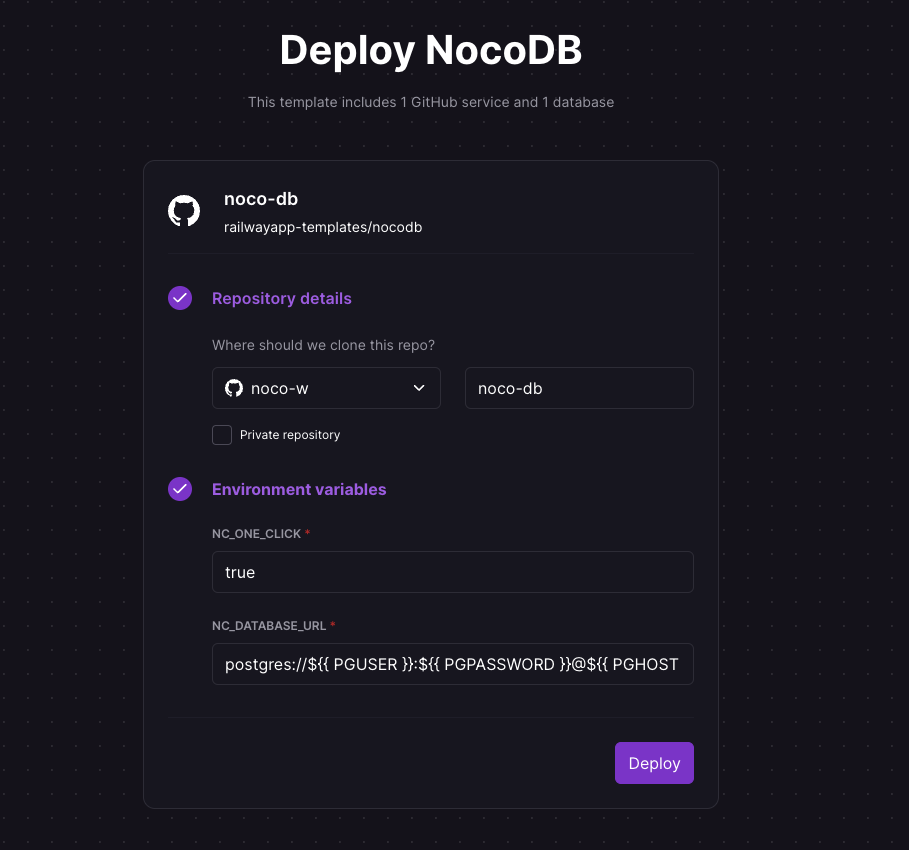 |
||||
|
||||
</details> |
||||
|
||||
### FreeBSD / FreeNAS / TrueNAS Jail |
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://gist.github.com/Zamana/e9281d736f9e9ce5882c6f4b140a590e) provided by [C. R. Zamana](https://github.com/Zamana). |
||||
|
||||
### Sealos |
||||
|
||||
[](https://cloud.sealos.io/?openapp=system-template%3FtemplateName%3Dnocodb) |
||||
|
||||
## Sample Demos |
||||
|
||||
### Code Sandbox |
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="100%" height="500" src="https://codesandbox.io/embed/vigorous-firefly-80kq5?hidenavigation=1&theme=dark" title="Code Sandbox" frameBorder="0" allow="clipboard-write"></iframe> |
||||
|
||||
### Docker deploying with one command |
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="100%" height="500" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/K-UEecQyiOk" title="YouTube video player" frameBorder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowFullScreen></iframe> |
||||
|
||||
### Using NPX |
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="100%" height="500" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/v6Nn75P1p7I" title="YouTube video player" frameBorder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowFullScreen></iframe> |
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Auto-Upstall' |
||||
description: 'Auto-Upstall is a one command setup for NocoDB installation.' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB one command installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Auto-Upstall |
||||
|
||||
> auto-upstall is one command that automatically installs and upgrades NocoDB with SSL setup. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
bash <(curl -sSL http://install.nocodb.com/noco.sh) <(mktemp) |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
The above command is the fastest and easiest way to self-host NocoDB on a server. It auto-generates a docker-compose for you behind the scenes. |
||||
|
||||
## Notes on Auto-Upstall |
||||
Auto-upstall is a single command that : 🕊 |
||||
- 🐳 First Automatically installs all pre-requisites on your linux based server (docker, docker-compose) |
||||
- 🚀 Then automatically installs |
||||
- 🇳 NocoDB, |
||||
- 🐘 PostgreSQL, |
||||
- ⚡ Redis, |
||||
- 🗄 Minio, |
||||
- 🌐 Traefik gateway. |
||||
- 🔄 Also automatically upgrades NocoDB when new versions are available. |
||||
- 🔒 And finally automatically setups+renews SSL. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick installation guide |
||||
|
||||
This is quick walkthrough of how to install NocoDB using auto-upstall script. |
||||
|
||||
- **Step 1** : 🔐 SSH into your server (Linux-based system - Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS etc.) |
||||
- **Step 2** : 🚀 Run the below command : |
||||
```bash |
||||
bash <(curl -sSL http://install.nocodb.com/noco.sh) <(mktemp) |
||||
``` |
||||
- **Step 3** : 🌐 Open your browser and go to URL |
||||
- For 🌍 HTTP: `http://<your-domain-or-ip>` |
||||
- For 🔒 HTTPS: `https://<your-domain-or-ip>` |
||||
- **Step 4** : 🐦 Don't keep the command a secret. Tweet how easy it is. This step is a must! |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> install.nocodb.com/noco.sh script can be found [here in our github](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nocodb/nocodb/develop/docker-compose/setup-script/noco.sh) |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Detailed installation guide |
||||
|
||||
1. Run the following command in your terminal: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
bash <(curl -sSL http://install.nocodb.com/noco.sh) <(mktemp) |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
3. Follow the installation prompts |
||||
- **Domain name**: Enter the IP address or domain name for your NocoDB instance. |
||||
- **SSL configuration**: If you entered a valid domain name, you'll be asked if you want to configure SSL. |
||||
- **Advanced options**: You can choose to show advanced options or use default settings. |
||||
|
||||
4. Advanced options (if chosen): |
||||
- Choose between community (CE) or enterprise edition (EE) |
||||
- Enter license key (for EE) |
||||
- Enable/disable Redis for caching |
||||
- Enable/disable Minio for file storage |
||||
- Configure Minio domain and SSL |
||||
- Enable/disable Watchtower for automatic updates |
||||
- Set the number of NocoDB instances to run |
||||
|
||||
5. Wait for installation to complete - takes about 2-5 minutes. |
||||
Once done, you'll see a success message with the URL to access your NocoDB instance. |
||||
|
||||
6. Access NocoDB |
||||
Open the URL provided in your browser to access NocoDB. |
||||
|
||||
7. Congratulations! You should now have a working installation of NocoDB. Enjoy using your new no-code database platform! |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation management menu |
||||
|
||||
After installation, you'll be asked if you want to start the management menu. This menu allows you to: |
||||
|
||||
- Start NocoDB |
||||
- Stop NocoDB |
||||
- View logs |
||||
- Restart NocoDB |
||||
- Upgrade NocoDB |
||||
- Scale NocoDB (change the number of running instances) |
||||
- Monitor NocoDB (view Docker stats) |
||||
|
||||
## Additional Notes |
||||
|
||||
- The script creates an update.sh file in the installation directory. You can use this to update NocoDB in the future. |
||||
- If you encounter any issues during installation, check the logs for error messages. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Docker' |
||||
description: 'Docker installation - takes about three minutes!' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB docker installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
Docker installation - takes about three minutes! |
||||
|
||||
Docker provides an easy way to install and run NocoDB. Follow these steps to get NocoDB up and running using Docker. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
- [Docker](https://www.docker.com/get-started) |
||||
|
||||
## Installation Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Choose your preferred database: |
||||
|
||||
<Tabs> |
||||
<TabItem value="sqlite" label="SQLite"> |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
docker run -d --name nocodb \ |
||||
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \ |
||||
-p 8080:8080 \ |
||||
nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="postgres" label="Postgres"> |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
docker run -d --name nocodb-postgres \ |
||||
-v "$(pwd)"/nocodb:/usr/app/data/ \ |
||||
-p 8080:8080 \ |
||||
-e NC_DB="pg://host.docker.internal:5432?u=root&p=password&d=d1" \ |
||||
-e NC_AUTH_JWT_SECRET="569a1821-0a93-45e8-87ab-eb857f20a010" \ |
||||
nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
</TabItem> |
||||
|
||||
</Tabs> |
||||
|
||||
2. Once the container is running, you can access NocoDB by opening http://localhost:8080 in your web browser. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
To persist data, always mount a volume at `/usr/app/data/`. Without this, your data will be lost when the container is removed. |
||||
|
||||
For versions prior to 0.10.6, mount the volume at /usr/src/app. |
||||
|
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting |
||||
|
||||
- If you can't access NocoDB after installation, check if the Docker container is running: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker ps |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
- If the container is not running, check the logs for any errors: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker logs nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
## Installation Video |
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="100%" height="500" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/K-UEecQyiOk" title="YouTube video player" frameBorder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" allowFullScreen></iframe> |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Docker Compose' |
||||
description: 'Install NocoDB using Docker Compose' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB docker installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Installing NocoDB with Docker Compose |
||||
|
||||
Docker Compose allows you to define and run multi-container Docker applications. It's a great way to set up NocoDB along with its database in a single configuration file. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
- [Docker](https://www.docker.com/get-started) |
||||
- [Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/) |
||||
|
||||
## Installation Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Clone the NocoDB repository from GitHub. |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
git clone https://github.com/nocodb/nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
2. Navigate to the docker-compose directory |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
cd nocodb/docker-compose/pg |
||||
``` |
||||
3. Start the services using Docker Compose: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker-compose up -d |
||||
``` |
||||
This will start NocoDB along with a PostgreSQL database. |
||||
|
||||
4. Access NocoDB in your browser by visiting `http://localhost:8080`. |
||||
|
||||
## Important Notes |
||||
|
||||
- The provided `docker-compose.yml` files are configured to persist data. Make sure the volumes are properly mounted. |
||||
- You can customize the `docker-compose.yml` file to change ports, environment variables, or add additional services. |
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting |
||||
|
||||
- If you encounter any issues, check the logs using the following command: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker-compose logs |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
- If you need to stop the services, use the following command: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker-compose down |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
- Ensure all required ports are available on your host machine. |
||||
|
||||
- For database connection issues, verify the database service is running: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker-compose ps |
||||
``` |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Homebrew' |
||||
description: 'Install NocoDB using Homebrew' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB homebrew installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Installing NocoDB with Homebrew |
||||
|
||||
Homebrew provides a simple way to install NocoDB on macOS and Linux systems. Follow these steps to install NocoDB using Homebrew. |
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
- [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/) |
||||
|
||||
## Installation Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Add the NocoDB tap to Homebrew: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
brew tap nocodb/nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
2. Install NocoDB: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
brew install nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
3. Start NocoDB: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
4. Access NocoDB in your browser by visiting `http://localhost:8080`. |
||||
|
||||
## Updating NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
To update NocoDB to the latest version, use the following command: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
brew upgrade nocodb |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting |
||||
|
||||
- If you encounter permission issues, make sure you have the necessary rights to install packages with Homebrew. |
||||
|
||||
- If NocoDB doesn't start, check if the default port (8080) is already in use. You can specify a different port using environment variables. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'AWS ECS (Fargate)' |
||||
description: 'AWS ECS (Fargate) Installation' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB AWS Fargate installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Deploying NocoDB on AWS ECS (Fargate) |
||||
|
||||
This guide will walk you through deploying NocoDB on Amazon ECS using Fargate. |
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
|
||||
- AWS CLI configured with appropriate permissions |
||||
- Basic understanding of AWS ECS and Fargate |
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Create ECS Cluster |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
aws ecs create-cluster --cluster-name <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
2. Create a Log Group: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
aws logs create-log-group --log-group-name /ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME> |
||||
``` |
||||
3. Create an ECS Task Definition: |
||||
|
||||
Every time you create it, it will add a new version. If it is not existing, the version will be 1. |
||||
```bash |
||||
aws ecs register-task-definition --cli-input-json file://task-definition.json |
||||
``` |
||||
:::tip |
||||
This json file defines the container specification. You can define secrets such as NC_DB and environment variables here. |
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
Example `task-definition.json`: |
||||
|
||||
```json |
||||
{ |
||||
"family": "nocodb-sample-task-def", |
||||
"networkMode": "awsvpc", |
||||
"containerDefinitions": [ |
||||
{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>", |
||||
"image": "nocodb/nocodb:latest", |
||||
"essential": true, |
||||
"logConfiguration": { |
||||
"logDriver": "awslogs", |
||||
"options": { |
||||
"awslogs-group": "/ecs/<YOUR_APP_NAME>/<YOUR_CONTAINER_NAME>", |
||||
"awslogs-region": "<YOUR_AWS_REGION>", |
||||
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs" |
||||
} |
||||
}, |
||||
"secrets": [ |
||||
{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_SECRETS_NAME>", |
||||
"valueFrom": "<YOUR_SECRET_ARN>" |
||||
} |
||||
], |
||||
"environment": [ |
||||
{ |
||||
"name": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME>", |
||||
"value": "<YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE_VALUE>" |
||||
} |
||||
], |
||||
"portMappings": [ |
||||
{ |
||||
"containerPort": 8080, |
||||
"hostPort": 8080, |
||||
"protocol": "tcp" |
||||
} |
||||
] |
||||
} |
||||
], |
||||
"requiresCompatibilities": [ |
||||
"FARGATE" |
||||
], |
||||
"cpu": "256", |
||||
"memory": "512", |
||||
"executionRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_EXECUTION_ROLE_ARN>", |
||||
"taskRoleArn": "<YOUR_ECS_TASK_ROLE_ARN>" |
||||
} |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create an ECS Service: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
aws ecs create-service \ |
||||
--cluster <YOUR_ECS_CLUSTER> \ |
||||
--service-name <YOUR_SERVICE_NAME> \ |
||||
--task-definition <YOUR_TASK_DEF>:<YOUR_TASK_DEF_VERSION> \ |
||||
--desired-count <DESIRED_COUNT> \ |
||||
--launch-type "FARGATE" \ |
||||
--platform-version <VERSION> \ |
||||
--health-check-grace-period-seconds <GRACE_PERIOD_IN_SECOND> \ |
||||
--network-configuration "awsvpcConfiguration={subnets=["<YOUR_SUBSETS>"], securityGroups=["<YOUR_SECURITY_GROUPS>"], assignPublicIp=ENABLED}" \ |
||||
--load-balancer targetGroupArn=<TARGET_GROUP_ARN>,containerName=<CONTAINER_NAME>,containerPort=<YOUR_CONTAINER_PORT> |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
:::tip |
||||
If your service fails to start, you may check the logs in ECS console or in Cloudwatch. Generally it fails due to the connection between ECS container and NC_DB. Make sure the security groups have the correct inbound and outbound rules. |
||||
::: |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Important Notes |
||||
|
||||
- Ensure that your security groups have the correct inbound and outbound rules. |
||||
- The NC_DB environment variable should be properly set to connect to your database. |
||||
- Monitor the ECS console and CloudWatch logs for any deployment issues. |
||||
- You can customize the task definition and service configuration based on your requirements. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'GCP Cloud Run' |
||||
description: 'Installing NocoDB on Google Cloud Run' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB Google Cloud run installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Deploying NocoDB on GCP Cloud Run |
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you deploy NocoDB on Google Cloud Platform using Cloud Run. |
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites |
||||
|
||||
- Google Cloud SDK installed and configured |
||||
- [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/) |
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Pull the NocoDB Docker image: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker pull nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
2. Tag the image for Google Container Registry (GCR): |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker tag nocodb/nocodb:latest gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
3. Push the image to GCR: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
docker push gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest |
||||
``` |
||||
4. Deploy NocoDB on Cloud Run: |
||||
|
||||
```bash |
||||
gcloud run deploy --image=gcr.io/<MY_PROJECT_ID>/nocodb/nocodb:latest \ |
||||
--region=us-central1 \ |
||||
--allow-unauthenticated \ |
||||
--platform=managed |
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
## Important Notes |
||||
|
||||
- Cloud Run only supports images from Google Container Registry (GCR) or Artifact registry. Hence we pull the image from Docker Hub and push it to GCR. |
||||
- Ensure that your GCP project has the necessary APIs enabled (Cloud Run, Container Registry). |
||||
- The `--allow-unauthenticated` flag is used to allow unauthenticated access to the service. You can remove this flag if you want to restrict access. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'DigitalOcean' |
||||
description: 'Installing NocoDB on Digital Ocean' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB Digital Ocean installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Deploying NocoDB as a DigitalOcean App |
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to deploy NocoDB on DigitalOcean using their App Platform. |
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Steps |
||||
|
||||
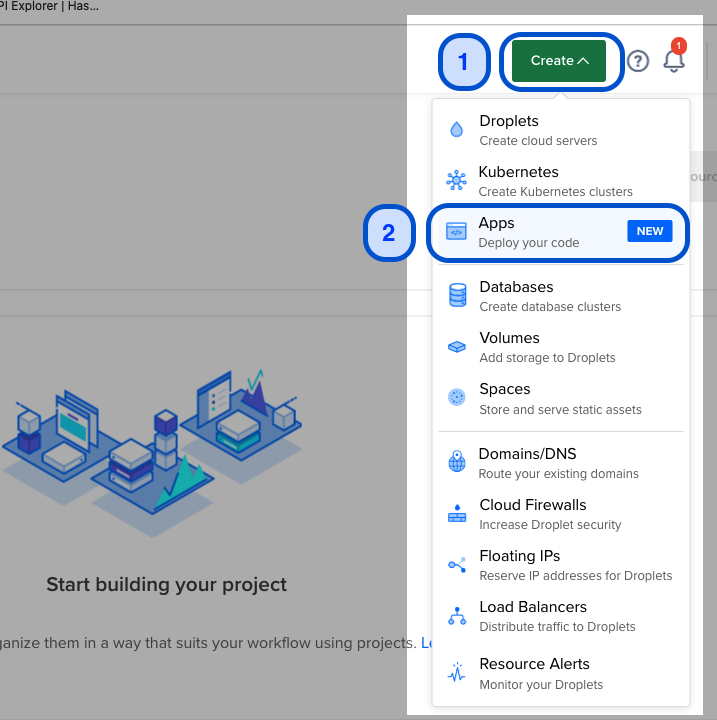
1. On the DigitalOcean homepage, click on the Create icon and select "Apps (Deploy your code)". |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790558-f8fe5580-5a58-412c-9c2e-145587712bf2.png) |
||||
2. Choose "Docker Hub" as the source. |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790563-b5b6d5b4-0bdc-4718-8cea-0a7ee52f283b.png) |
||||
|
||||
3. Set the source repository as nocodb/nocodb. You can optionally specify a release tag if you want a specific NocoDB version. |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790564-1dcb5e33-3a57-471a-a44c-835a410a0cb7.png) |
||||
|
||||
4. Configure any additional settings as needed. |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790565-c0234b2e-ad50-4042-90b6-4f8798f1d585.png) |
||||
|
||||
5. Name your web service and select the nearest region for cloud hosting. |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790567-a6e65e4e-9aa0-4edb-998e-da8803ad6e23.png) |
||||
|
||||
6. Choose your preferred hosting plan and click on "Launch Basic App". |
||||
|
||||
[](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/86527202/154790570-62044713-5cca-4d06-82ec-f3cc257218a1.png) |
||||
|
||||
Your application will be built, and the URL will be live shortly. The URL will look something like https://your-app-name.ondigitalocean.app/. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Important Notes |
||||
|
||||
- Ensure you configure environment variables for database connections if needed. |
||||
- Set up persistent storage for your NocoDB data. |
||||
- You can scale your app as needed using DigitalOcean's App Platform. |
||||
- Consider enabling automatic deployments for easier updates. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Other Installation Methods' |
||||
description: 'Installing NocoDB on other platforms' |
||||
tags: ['Open Source'] |
||||
keywords : ['NocoDB installation', 'NocoDB Digital Ocean installation', 'NocoDB prerequisites'] |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Installing NocoDB on Other Platforms |
||||
|
||||
This guide covers installation methods for NocoDB on various platforms including Cloudron, CapRover, Railway, FreeBSD/FreeNAS/TrueNAS Jail, and SealOs. |
||||
|
||||
## Cloudron |
||||
|
||||
Cloudron provides an easy way to install and manage NocoDB. |
||||
|
||||
### Installation Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to your Cloudron dashboard. |
||||
2. Navigate to the App Store. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
3. Search for NocoDB |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
4. Click on the NocoDB app, then click "Install". |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
5. Configure NocoDB settings as needed. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
5. Once installed, go to "My Apps" and launch NocoDB. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
### Important Notes |
||||
- Ensure your Cloudron server meets the minimum requirements for running NocoDB. |
||||
- Configure backups for your NocoDB instance through Cloudron's backup system. |
||||
- Keep your Cloudron and NocoDB app up to date for the latest features and security patches. |
||||
|
||||
## CapRover |
||||
|
||||
### Deployment Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to your CapRover dashboard. |
||||
2. Go to "Apps" and click on "One-Click Apps/Databases". |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
3. Search for NocoDB and click on it. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
4. Click on NocoDB to start the configuration process. |
||||
5. Configure NocoDB settings as needed and click "Deploy". |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
6. Once deployed, you can access NocoDB from the provided URL. |
||||
|
||||
### Important Notes |
||||
- Ensure your CapRover server has sufficient resources to run NocoDB. |
||||
- Configure persistent storage for your NocoDB data. |
||||
- Set up SSL for secure access to your NocoDB instance. |
||||
- Regularly update your CapRover server and NocoDB app for the latest features and security patches. |
||||
|
||||
## Railway |
||||
|
||||
### Deployment Steps |
||||
|
||||
1. Go to Railway Templates. |
||||
2. Search for "NocoDB" in the templates list. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
3. Click on the NocoDB template, then click "Deploy". |
||||
4. Configure your NocoDB settings as needed. |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
5. Railway will automatically deploy your NocoDB instance. |
||||
|
||||
### Important Notes |
||||
- Make sure to configure environment variables for database connections if needed. |
||||
- Set up persistent storage for your NocoDB data. |
||||
- Regularly update your NocoDB instance for the latest features and security patches. |
||||
|
||||
## FreeBSD/FreeNAS/TrueNAS Jail Installation |
||||
|
||||
For detailed instructions on installing NocoDB on FreeBSD, FreeNAS, or TrueNAS Jail, please refer to the [guide](https://gist.github.com/Zamana/e9281d736f9e9ce5882c6f4b140a590e) provided by [C. R. Zamana.](https://github.com/Zamana) |
||||
|
||||
## Sealos |
||||
|
||||
1. Open the NocoDB template by clicking on the following button: |
||||
|
||||
[](https://cloud.sealos.io/?openapp=system-template%3FtemplateName%3Dnocodb) |
||||
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to configure and deploy your NocoDB instance. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
{ |
||||
"label": "Installation", |
||||
"collapsible": true, |
||||
"collapsed": false, |
||||
"link": { |
||||
"type": "generated-index" |
||||
} |
||||
} |
||||
Loading…
Reference in new issue