|
|
4 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | 4 years ago | |
| center_the_window.gif | ||
| current_window.gif | ||
| focus_the_window.gif | ||
| scaling_factor.jpg | ||
| window_attr.gif | ||
| window_state.gif | ||
README.md
Top level windows management
What is covered
In this tutorial we will show you how to work with windows using Compose for Desktop.
Windows creation
The main class for creating windows is AppWindow. The easiest way to create and launch a new window is to use an instance of the AppWindow class and call its method show(). You can see an example below:
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppWindow
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater
fun main() = invokeLater {
AppWindow().show {
// Content
}
}
Note that AppWindow should be created in AWT Event Thread. Instead of calling invokeLater() explicitly you can use Window DSL:
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
fun main() {
Window {
// Content
}
}
There are two types of window – modal and regular. Below are the functions for creating each type of window:
- Window – regular window type.
- Dialog – modal window type. Such a window locks its parent window until the user completes working with it and closes the modal window.
You can see an example of both types of window below.
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.runtime.remember
import androidx.compose.ui.window.v1.Dialog
fun main() {
Window {
val dialogState = remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Button(onClick = { dialogState.value = true }) {
Text(text = "Open dialog")
}
if (dialogState.value) {
Dialog(
onDismissRequest = { dialogState.value = false }
) {
// Dialog's content
}
}
}
}
Window attributes
Each window has following parameters, all of them could be omitted and have default values:
- title – window title
- size – initial window size
- location – initial window position
- centered – set the window to the center of the display
- icon – window icon
- menuBar – window context menu
- undecorated – disable native border and title bar of the window
- resizable – makes the window resizable or unresizable
- events – window events
- onDismissEvent – event when removing the window content from a composition
An example of using window parameters in the creation step:
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppManager
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.desktop.WindowEvents
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.ExperimentalComposeUiApi
import androidx.compose.ui.input.key.Key
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntSize
import androidx.compose.ui.window.v1.MenuItem
import androidx.compose.ui.window.v1.KeyStroke
import androidx.compose.ui.window.v1.Menu
import androidx.compose.ui.window.v1.MenuBar
import java.awt.Color
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class)
fun main() {
val count = mutableStateOf(0)
val windowPos = mutableStateOf(IntOffset.Zero)
Window(
title = "MyApp",
size = IntSize(400, 250),
location = IntOffset(100, 100),
centered = false, // true - by default
icon = getMyAppIcon(),
menuBar = MenuBar(
Menu(
name = "Actions",
MenuItem(
name = "Increment value",
onClick = {
count.value++
},
shortcut = KeyStroke(Key.I)
),
MenuItem(
name = "Exit",
onClick = { AppManager.exit() },
shortcut = KeyStroke(Key.X)
)
)
),
undecorated = true, // false - by default
events = WindowEvents(
onRelocate = { location ->
windowPos.value = location
}
)
) {
// content
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column {
Text(text = "Location: ${windowPos.value} Value: ${count.value}")
Button(
onClick = {
AppManager.exit()
}
) {
Text(text = "Close app")
}
}
}
}
}
fun getMyAppIcon() : BufferedImage {
val size = 256
val image = BufferedImage(size, size, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB)
val graphics = image.createGraphics()
graphics.color = Color.orange
graphics.fillOval(0, 0, size, size)
graphics.dispose()
return image
}
Window properties
AppWindow parameters correspond to the following properties:
- title – window title
- width – window width
- height – window height
- x – position of the left top corner of the window along the X axis
- y – position of the left top corner of the window along the Y axis
- resizable - returns
trueif the window resizable,falseotherwise - icon – window icon image
- events – window events
To get the properties of a window, it is enough to have a link to the current or specific window. There are two ways to get the current focused window:
- Using the global environment:
import androidx.compose.desktop.LocalAppWindow
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
fun main() {
val windowPos = mutableStateOf(IntOffset.Zero)
Window {
val current = LocalAppWindow.current
// Content
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column {
Text(text = "Location: ${windowPos.value}")
Button(
onClick = {
windowPos.value = IntOffset(current.x, current.y)
}
) {
Text(text = "Print window location")
}
}
}
}
}
- Using AppManager:
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppManager
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntOffset
fun main() {
val windowPos = mutableStateOf(IntOffset.Zero)
Window {
// Content
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column {
Text(text = "Location: ${windowPos.value}")
Button(
onClick = {
val current = AppManager.focusedWindow
if (current != null) {
windowPos.value = IntOffset(current.x, current.y)
}
}
) {
Text(text = "Print window location")
}
}
}
}
}
Using the following methods, you can change the properties of the AppWindow:
- setTitle(title: String) – window title
- setSize(width: Int, height: Int) – window size
- setLocation(x: Int, y: Int) – window position
- setWindowCentered() – set the window to the center of the display
- setIcon(image: BufferedImage?) – window icon
- setMenuBar(menuBar: MenuBar) - window menu bar
import androidx.compose.desktop.LocalAppWindow
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.material.Button
fun main() {
Window {
val window = LocalAppWindow.current
// Content
Button(
onClick = {
window.setWindowCentered()
}
) {
Text(text = "Center the window")
}
}
}
Methods
Using the following methods, you can change the state of the AppWindow:
- show(parentComposition: CompositionReference? = null, content: @Composable () -> Unit) – shows a window with the given Compose content,
parentCompositionis the parent of this window's composition. - close() - closes the window.
- minimize() - minimizes the window to the taskbar. If the window is in fullscreen mode this method is ignored.
- maximize() - maximizes the window to fill all available screen space. If the window is in fullscreen mode this method is ignored.
- makeFullscreen() - switches the window to fullscreen mode if the window is resizable. If the window is in fullscreen mode
minimize()andmaximize()methods are ignored. - restore() - restores the normal state and size of the window after maximizing/minimizing/fullscreen mode.
You can know about window state via properties below:
- isMinimized - returns true if the window is minimized, false otherwise.
- isMaximized - returns true if the window is maximized, false otherwise.
- isFullscreen - returns true if the window is in fullscreen state, false otherwise.
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.size
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Spacer
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppManager
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppWindow
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater
fun main() = invokeLater {
AppWindow().show {
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(top = 20.dp, bottom = 20.dp)
) {
Button("Minimize", { AppManager.focusedWindow?.minimize() })
Button("Maximize", { AppManager.focusedWindow?.maximize() })
Button("Fullscreen", { AppManager.focusedWindow?.makeFullscreen() })
Button("Restore", { AppManager.focusedWindow?.restore() })
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
Button("Close", { AppManager.focusedWindow?.close() })
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun Button(text: String = "", action: (() -> Unit)? = null) {
Button(
modifier = Modifier.size(150.dp, 30.dp),
onClick = { action?.invoke() }
) {
Text(text)
}
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(10.dp))
}
Window events
Events can be defined using the events parameter in the window creation step or redefine using the events property at runtime. Actions can be assigned to the following window events:
- onOpen – event during window opening
- onClose – event during window closing
- onMinimize – event during window minimizing
- onMaximize – event during window maximizing
- onRestore – event during restoring window size after window minimize/maximize
- onFocusGet – event when window gets focus
- onFocusLost – event when window loses focus
- onResize – event on window resize (argument is window size as IntSize)
- onRelocate – event of the window reposition on display (argument is window position as IntOffset)
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.desktop.WindowEvents
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.IntSize
fun main() {
val windowSize = mutableStateOf(IntSize.Zero)
val focused = mutableStateOf(false)
Window(
events = WindowEvents(
onFocusGet = { focused.value = true },
onFocusLost = { focused.value = false },
onResize = { size ->
windowSize.value = size
}
)
) {
// Content
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Text(text = "Size: ${windowSize.value} Focused: ${focused.value}")
}
}
}
AppManager
The AppManager singleton is used to customize the behavior of the entire application. Its main features:
- Description of common application events
AppManager.setEvents(
onAppStart = { println("onAppStart") }, // Invoked before the first window is created
onAppExit = { println("onAppExit") } // Invoked after all windows are closed
)
- Customization of common application context menu
AppManager.setMenu(
getCommonAppMenuBar() // Custom function that returns MenuBar
)
- Access to the application windows list
val windows = AppManager.windows
- Getting the current focused window
val current = AppManager.focusedWindow
- Application exit
AppManager.exit() // Closes all windows
Access to Swing components
Compose for Desktop is tightly integrated with Swing at the top-level windows layer. For more detailed customization, you can access the JFrame class:
import androidx.compose.desktop.AppManager
import androidx.compose.desktop.Window
import androidx.compose.material.Text
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.material.Button
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
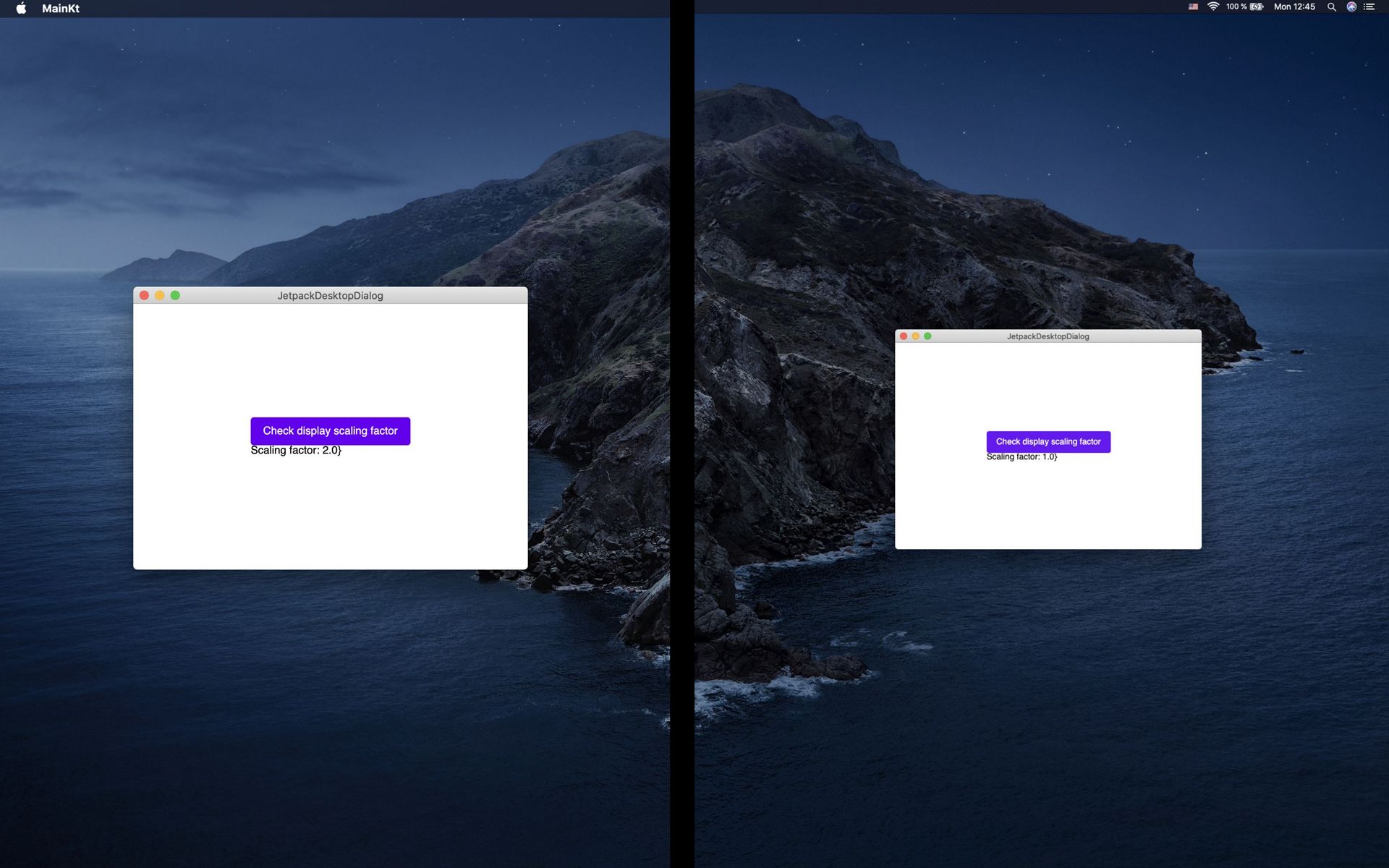
fun main() {
val scaleFactor = mutableStateOf(0.0)
Window {
// Content
Box(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Column {
Button(
onClick = {
val current = AppManager.focusedWindow
if (current != null) {
val jFrame = current.window
// Do whatever you want with it
scaleFactor.value = jFrame.graphicsConfiguration.defaultTransform.scaleX
}
}
) {
Text(text = "Check display scaling factor")
}
Text(text = "Scaling factor: ${scaleFactor.value}")
}
}
}
}